LSS1-1:
From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
Living things are made of cells; either one cell or many different numbers and types of cells
- List at least 10 organisms that are made of cells.
- Describe a cell in simple terms.
- In what ways are most animal cells and most plant cells similar?
- In what ways are most animal cells and most plant cells different?
- List several places you might expect to find single-cell organisms.
- What do cells need to survive?
- Why do you think some cells are shaped differently from others?
- Compare two types of cells in the human body.
- How do you think the discovery of cells changed our understanding of living things?
- How might advancements in technology and research help us better understand cells in the future?
Common Misconceptions
Misconceptions about Cells identified by Open AI ChatGPT
Cells are only found in living things that move or have organs: Students may think that only animals have cells or that only complex organisms have cells, but in reality, all living things, including plants, fungi, and even bacteria, are made up of cells.
All cells are the same: Students may think that all cells are identical, but in fact, there are many different types of cells with different shapes, sizes, and functions. For example, red blood cells are specialized for carrying oxygen, while nerve cells are specialized for transmitting electrical signals.
Cells are too small to see: While cells are incredibly small, they are not invisible. With the help of a microscope, it is possible to see individual cells and observe their structures and behaviors.
Cells are static and unchanging: Students may think that cells are static and unchanging, but in reality, cells are constantly growing, dividing, and adapting to their environments.
Cells are all the same age: Students may think that all the cells in their body are the same age, but in fact, cells in different parts of the body can be different ages. For example, skin cells are constantly being replaced, while neurons in the brain can last a lifetime.
Cells can survive on their own: Students may think that cells can survive on their own outside of an organism, but in reality, most cells rely on a complex system of support and communication with other cells to function properly.
Cells are all shaped like circles: Students may think that all cells are round like a ball, but in fact, cells can come in many different shapes, including flat, elongated, and irregular shapes.
Cells are simple structures: Cells are actually highly complex and organized structures, containing a variety of specialized organelles and biomolecules that carry out specific functions.
All cells are the same: Not all cells are the same. There are many different types of cells, each with their own unique characteristics and functions. For example, human cells are different than plant cells, and nerve cells are different than muscle cells.
Cells are visible to the naked eye: Most cells are too small to be seen without the aid of a microscope.
Cells are passive structures: Cells are actually highly active structures that are constantly carrying out a variety of metabolic processes.
Dead cells can be brought back to life: Once a cell dies, it cannot be brought back to life. The death of a cell is permanent and irreversible.
All living organisms are made of one type of cell: Multicellular organisms are made of various types of cells which perform different functions, for example, nerve cells, muscle cells and blood cells.

List at least 10 organisms that are made of cells.

A cell is the fundamental unit of life, comprising all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of an organism that retains the characteristics of life, and is capable of growth, metabolism, response to stimuli, and reproduction.
How would you describe a cell in a simple way for a much younger child?
Common Misconceptions
Misconceptions about single-celled organisms identified by Open AI ChatGPT
- Plant and animal cells are identical: Some students may think that plant and animal cells are exactly the same. While they share many similarities, such as having a nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles, they also have some key differences.
- Plant cells have a unique type of mitochondria: Some students may think that the mitochondria in plant cells are fundamentally different from those in animal cells, but they are actually very similar.
- Only animal cells have centrioles: While centrioles are present in animal cells, they are absent in most plant cells. However, some plant cells, such as those in green algae, do have centrioles.
- Chloroplasts are present in all plant cells: While most plant cells do have chloroplasts, not all do. For example, the roots and stem of a plant do not contain chloroplasts.
- Plant and animal cells have totally different functions: While there are some differences in the functions of plant and animal cells, they share many common functions such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste removal.
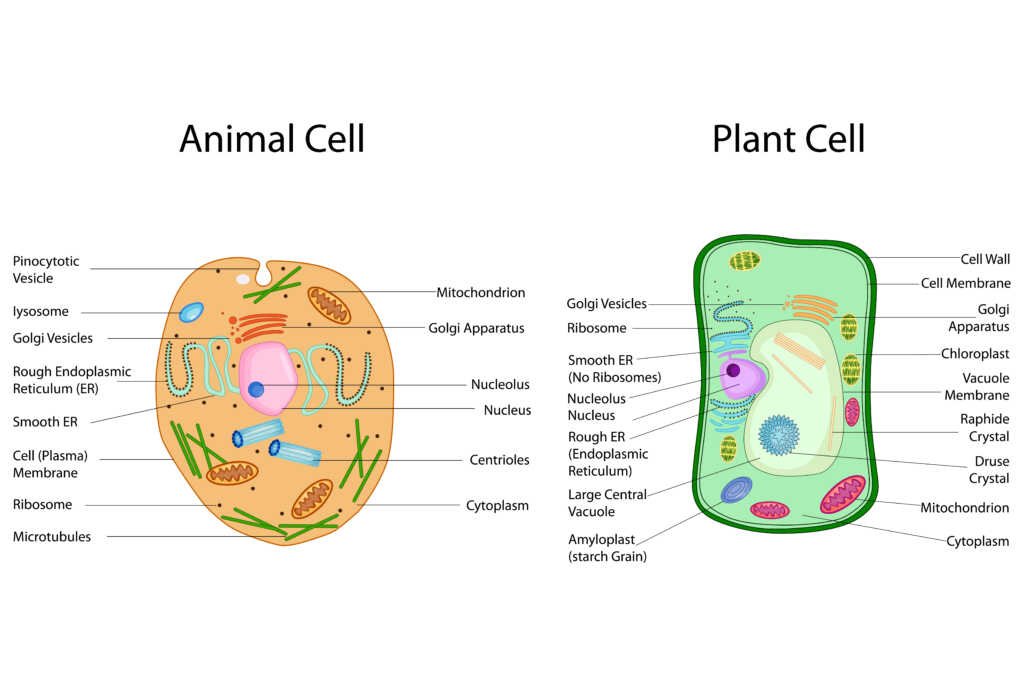
In what ways are most animal cells and most plant cells different?
Common Misconceptions
Misconceptions about single-celled organisms identified by Open AI ChatGPT
- Plant and animal cells are identical: Some students may think that plant and animal cells are exactly the same. While they share many similarities, such as having a nucleus, mitochondria, and other organelles, they also have some key differences.
- Plant cells have a unique type of mitochondria: Some students may think that the mitochondria in plant cells are fundamentally different from those in animal cells, but they are actually very similar.
- Only animal cells have centrioles: While centrioles are present in animal cells, they are absent in most plant cells. However, some plant cells, such as those in green algae, do have centrioles.
- Chloroplasts are present in all plant cells: While most plant cells do have chloroplasts, not all do. For example, the roots and stem of a plant do not contain chloroplasts.
- Plant and animal cells have totally different functions: While there are some differences in the functions of plant and animal cells, they share many common functions such as energy production, protein synthesis, and waste removal.

Common Misconceptions
Misconceptions about single-celled organisms identified by Open AI ChatGPT
All single-celled organisms are bacteria: While bacteria are a type of single-celled organism, there are other types of single-celled organisms, such as protists and archaea.
Single-celled organisms are not complex: While single-celled organisms may appear simple, they can be very complex and have intricate cellular processes.
Single-celled organisms do not have specialized cells: While single-celled organisms may not have specialized cells like multicellular organisms, they can have specialized organelles that perform specific functions.
All single-celled organisms are harmful: While some single-celled organisms, such as certain bacteria, can be harmful to humans, many single-celled organisms are beneficial or neutral.
Single-celled organisms do not interact with their environment: Single-celled organisms are capable of responding to changes in their environment and can carry out a variety of behaviors such as movement, chemotaxis, and phototaxis.
Single-celled organisms do not have a nucleus: Some single-celled organisms, such as bacteria, do not have a nucleus, but others, such as protists, do have a nucleus.
Single-celled organisms cannot evolve: Single-celled organisms are capable of evolving and adapting to their environment over time, just like multicellular organisms.

Why do you think some cells are shaped differently from others?
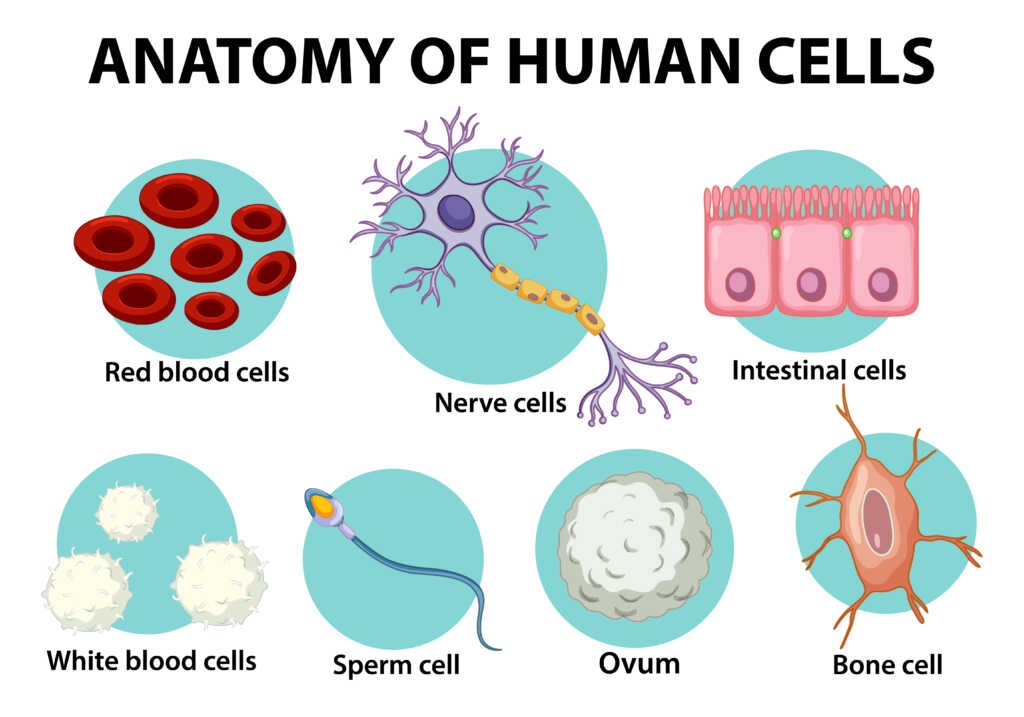
Compare two types of cells in the human body.
Explain why each is well-suited for its jobs.

This drawing by Robert Hooke in 1665 shows cork cells under a microscope.
(Note: the microscope was a new invention at the time!)
How do you think the discovery of cells changed our understanding of living things?

How might advancements in technology and research help us better understand cells in the future?

