LSS1-2:
From Molecules to Organisms
Function of a cell as a whole and parts of the cell
- List several ways a cell is like a school.
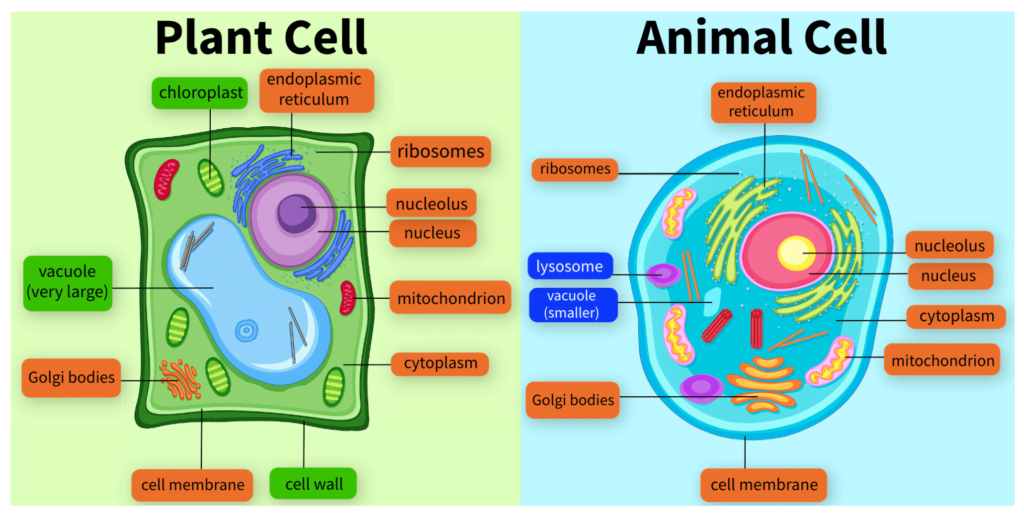
- List several ways that most plant cells and most animal cells are similar.
- List several ways that most plant cells and most animal cells are different.
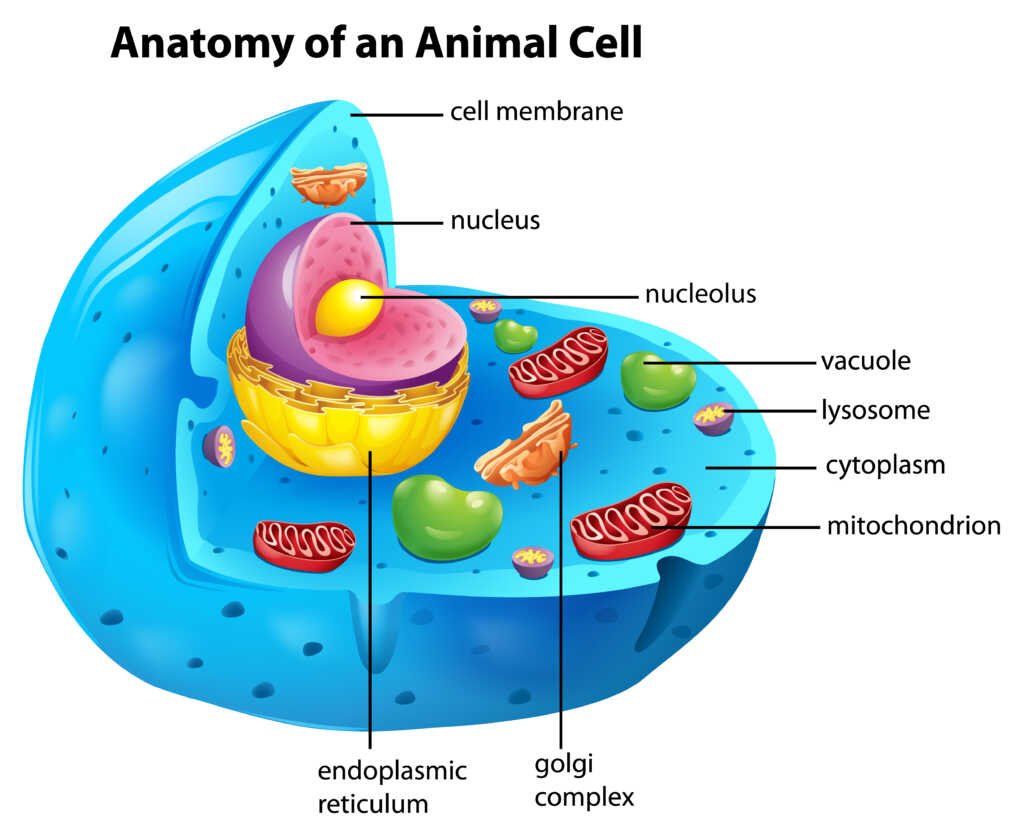
- How do different parts of the cell work together to maintain homeostasis, or a stable internal environment, in the cell?
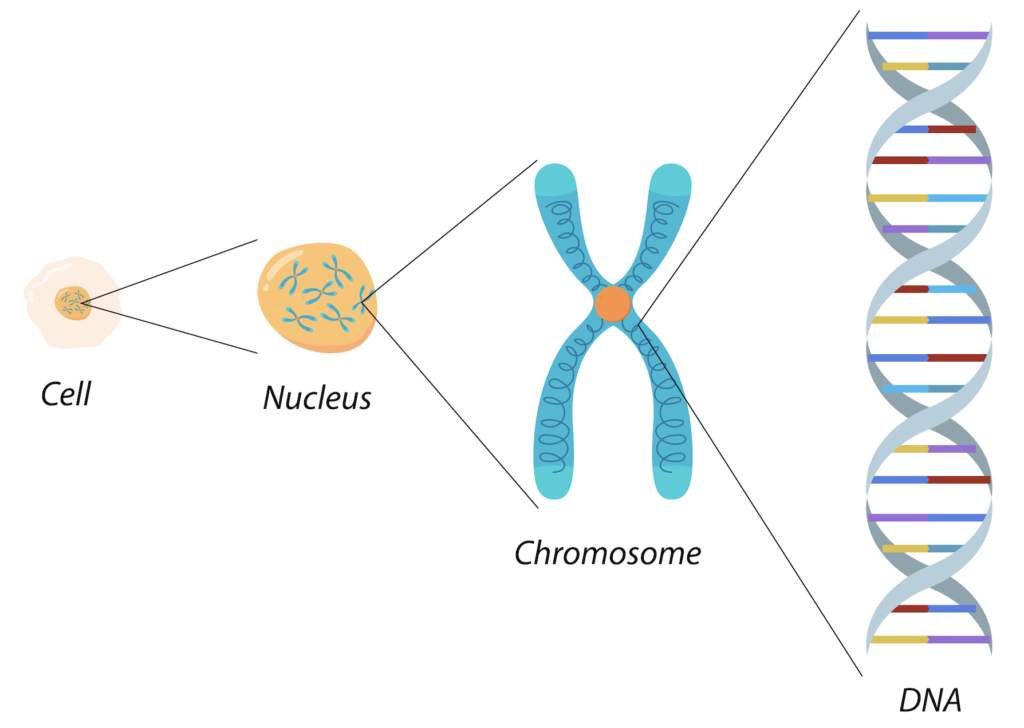
- Why is DNA so important to every cell in every organism?
- Write a short story from the perspective of any cell organelle.

List several ways a cell is like a school.
How do different parts of the cell work together to maintain homeostasis, or a stable internal environment, in the cell?
Why is DNA so important to every cell in every organism?
Write a short story from the perspective of any cell organelle.