For optimal viewing experience, it is recommended to access this page on a computer or large tablet.
BELLRINGERS
ESS2: Earth's Systems
MS ESS2-4
Cycling of Water Through Earth's Systems
- Where do you think most of Earth's fresh water is located?
- How does a warming climate cause sea levels to rise?
- Explain how water in a puddle can eventually be part of the water in a cloud.
- How does fog form?
- What does it feel like inside a cloud? What state(s) of matter are clouds?
- Describe all the forms of water you see in this picture.
- Why doesn't Lake Erie dry out?
- Why is grass often wet with dew in the morning but dry by the afternoon?
- Which direction does the Amazon River flow?
- Which direction does the Nile River flow?

Where do you think most of the fresh water is located?
Common Misconceptions
There is an unlimited supply of fresh water: In reality, only about 2.5% of the Earth’s water is fresh and accessible for human use. The majority of the Earth’s water is saltwater in the oceans.
All fresh water is safe to drink: Not all fresh water sources are safe for drinking. Many contain pollutants and bacteria that can make people sick.
Water can be made fresh by adding chemicals: While certain chemicals can help purify water, they cannot make saltwater or polluted water safe to drink.
Rainwater is always safe to drink: While rainwater is often considered pure, it can also collect pollutants from the air and surfaces it lands on.
Freshwater is only found in lakes and rivers: Freshwater can also be found underground in aquifers and in glaciers.
Water scarcity is only an issue in developing countries: Water scarcity is a global problem, with many developed countries also facing water shortages and droughts.
Additional Resources
Common Misconceptions
Climate change is not real: This is not true. The overwhelming majority of scientists agree that the Earth’s climate is changing and that human activity, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, is the primary cause.
The sea levels are not rising: This is also not true. Sea levels have been rising for the last century, and the rate of sea level rise is increasing.
Sea level rise is only happening in certain areas: While some areas may be experiencing more sea level rise than others, sea level rise is happening globally.
Rising sea levels only affects small island countries: Rising sea levels can have significant impacts on coastal communities and infrastructure around the world, regardless of the size or location of the country.
Climate change and sea level rise can be stopped by planting trees or reducing carbon footprint alone: While these actions can help slow down the process, they are not enough to stop it completely. Deeper systemic changes are needed.

Include a labeled diagram in your explanation.
Common Misconceptions
Clouds are made of water in the gas state: Clouds are actually made up of a mixture of water droplets and ice crystals.
Clouds form only when it’s hot outside: Clouds can form at any temperature, as long as there is enough moisture in the air and enough cloud condensation nuclei for the water vapor to condense around.
Clouds form only high in the atmosphere: Clouds can form at many different altitudes, from just a few feet above the ground to over 50,000 feet in the sky.
Clouds are static: Clouds are constantly moving and changing shape as they are influenced by wind, temperature and humidity.
- More meteorology misconceptions: New Tab

What causes it to form?
Include a diagram that shows how you think fog forms as part of your explanation.
Common Misconceptions
Fog is a cloud that comes down to the ground from the sky. In reality, fog is a cloud that forms at ground level and is made up of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air.
That fog is always cold. While fog can lower the temperature in an area, it is not always cold. The temperature of fog depends on the temperature of the air and the humidity.
That fog is caused by pollution. While pollution can contribute to the formation of fog, it is not the only cause. Fog can also form due to natural causes such as temperature inversion and evaporation.

What state(s) of matter do you think make up clouds? Solid, Liquid, and/or Gas?
Common Misconceptions
Fog is a cloud that comes down to the ground from the sky. In reality, fog is a cloud that forms at ground level and is made up of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air.
That fog is always cold. While fog can lower the temperature in an area, it is not always cold. The temperature of fog depends on the temperature of the air and the humidity.
That fog is caused by pollution. While pollution can contribute to the formation of fog, it is not the only cause. Fog can also form due to natural causes such as temperature inversion and evaporation.

In what ways would this spot on the Earth look different the next day? How about several months later?
Common Misconceptions
The water cycle only involves precipitation and evaporation: The water cycle also includes the movement of water through the atmosphere, over land, and underground.
The water cycle is a steady process: The water cycle can vary in speed and intensity depending on factors such as temperature, precipitation, and evapotranspiration.
The water cycle only occurs in certain regions: The water cycle occurs globally and is a fundamental component of the Earth’s climate system.
Water is lost from the water cycle: Water is not lost from the water cycle, but instead it is constantly recycled through the different stages of the water cycle.
The water cycle is only driven by the sun: The water cycle is driven by many factors, including solar radiation, temperature, and topography.
Additional Resources
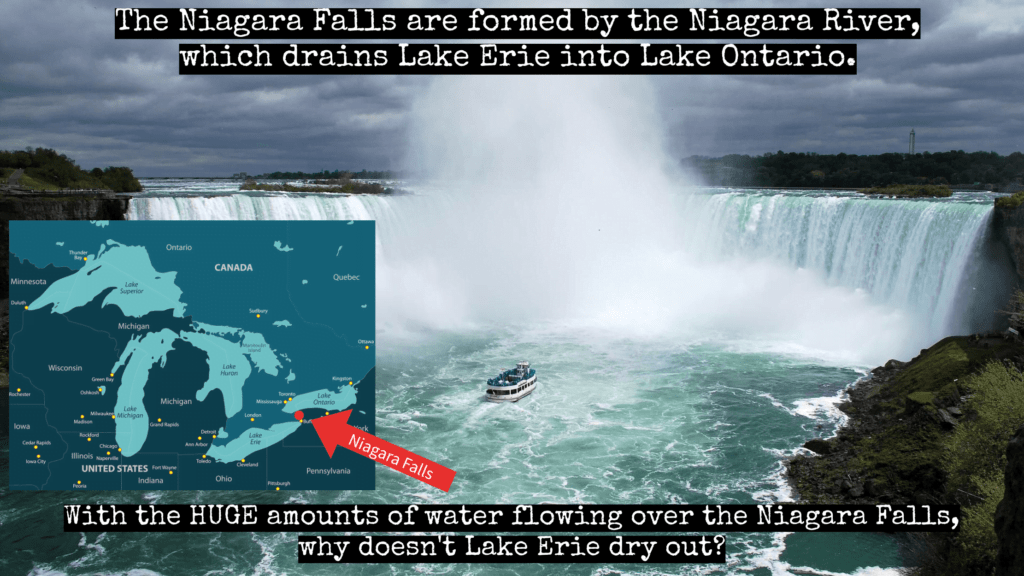
With the HUGE amounds of water flowing over the Niagara Falls, why doesn't lake Erie dry out?
Common Misconceptions
Niagara Falls never stops flowing: The flow of Niagara Falls is actually controlled by the hydroelectric power plants upstream. The flow can be reduced or stopped for maintenance or during low demand for electricity.
Additional Resources

How does the water get on the grass and then where does it go?
Common Misconceptions
Additional Resources
Kmusser, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
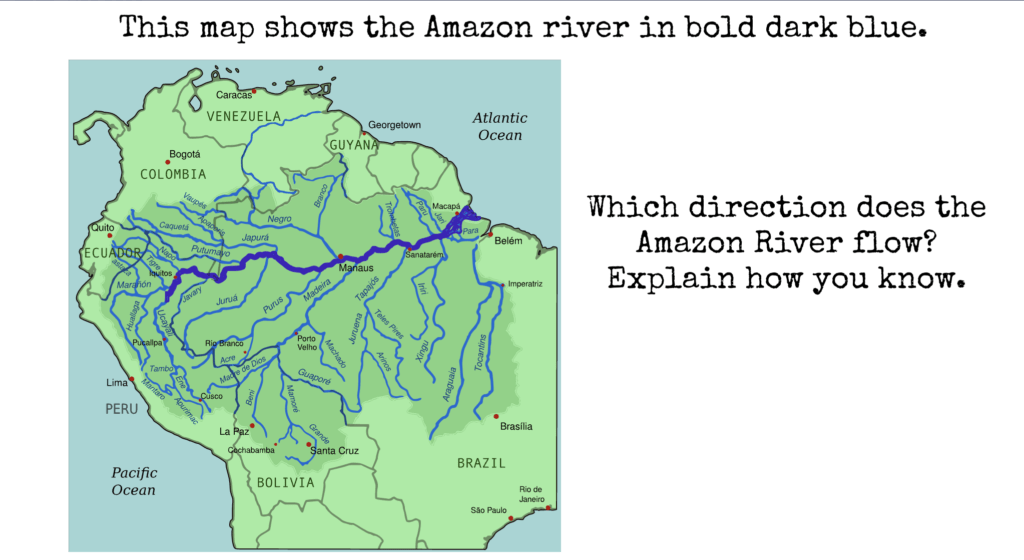
Explain how you know.
Common Misconceptions
Additional Resources
Hel-hama, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
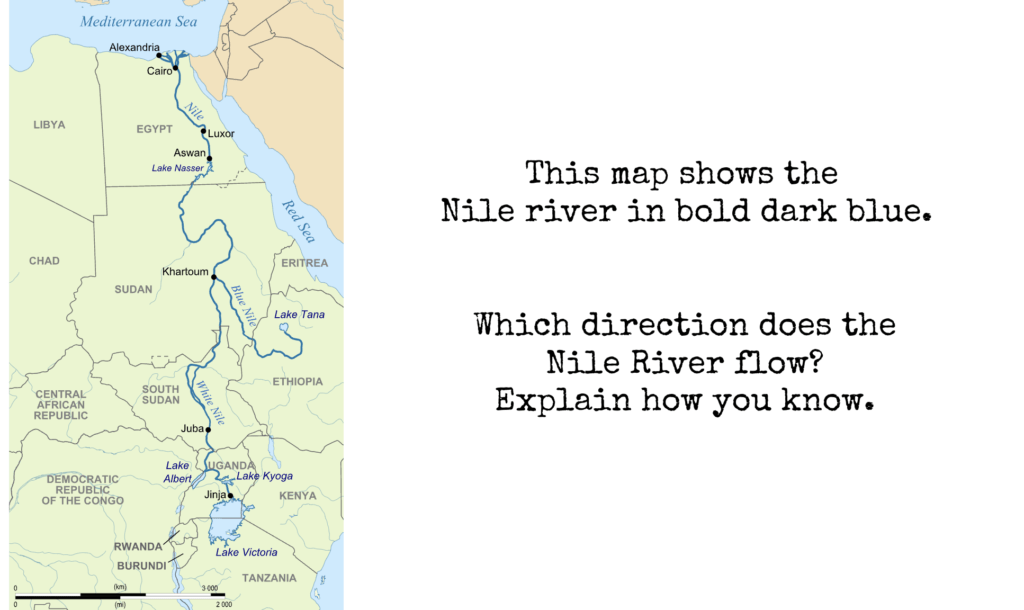
Common Misconceptions
Additional Resources


